Aqueous lithium-ion battery (LiB) electrode
with a voltage of 3.5 V.
Award-winning achievements
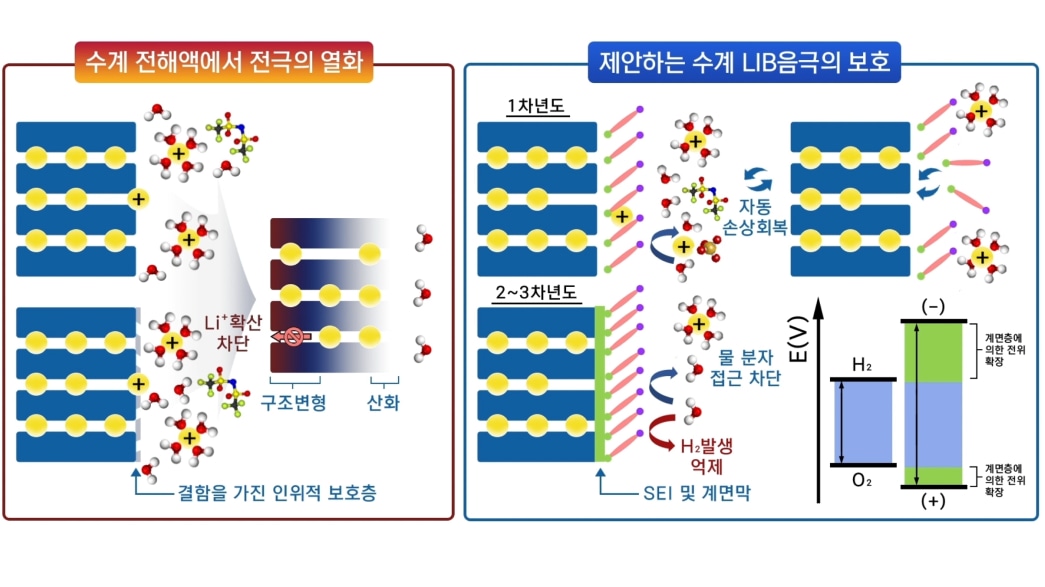
The development of LiBs for use in electric vehicles and energy storage systems has accelerated after the carbon-neutral declaration. However, conventional LiBs that use non-aqueous electrolytes have issues with frequent fire incidents and high costs, which urgently requires improvements in stability and cost competitiveness.
To address these problems, Prof. Hye Ryung Byon’s team aims to develop a LiB that uses an aqueous electrolyte, with the goal of developing an aqueous LiB electrode that is stable, cost-competitive, and has energy density and cycle performance similar to that of non-aqueous LiBs. Specifically, the research focuses on modifying the interface between the aqueous electrolyte and electrode to develop an aqueous battery with a voltage of about 3.5 V.
The results of this research can be applied to develop LiBs that are suitable for the ESS market and contribute to both fundamental and applied research through in-depth interface research. Understanding the electrochemical reactions between water and the electrode at the interface, as well as the electrical double layer structure, is expected to lay the foundation for future research on aqueous LiBs.