Electrolyte-Interface Reorganization Strategy for High-Efficiency Dual-ion Battery

-
Affiliation
Sogang University Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-
E-Mail
jryu@sogang.ac.kr
- Homepage
Award-winning achievements
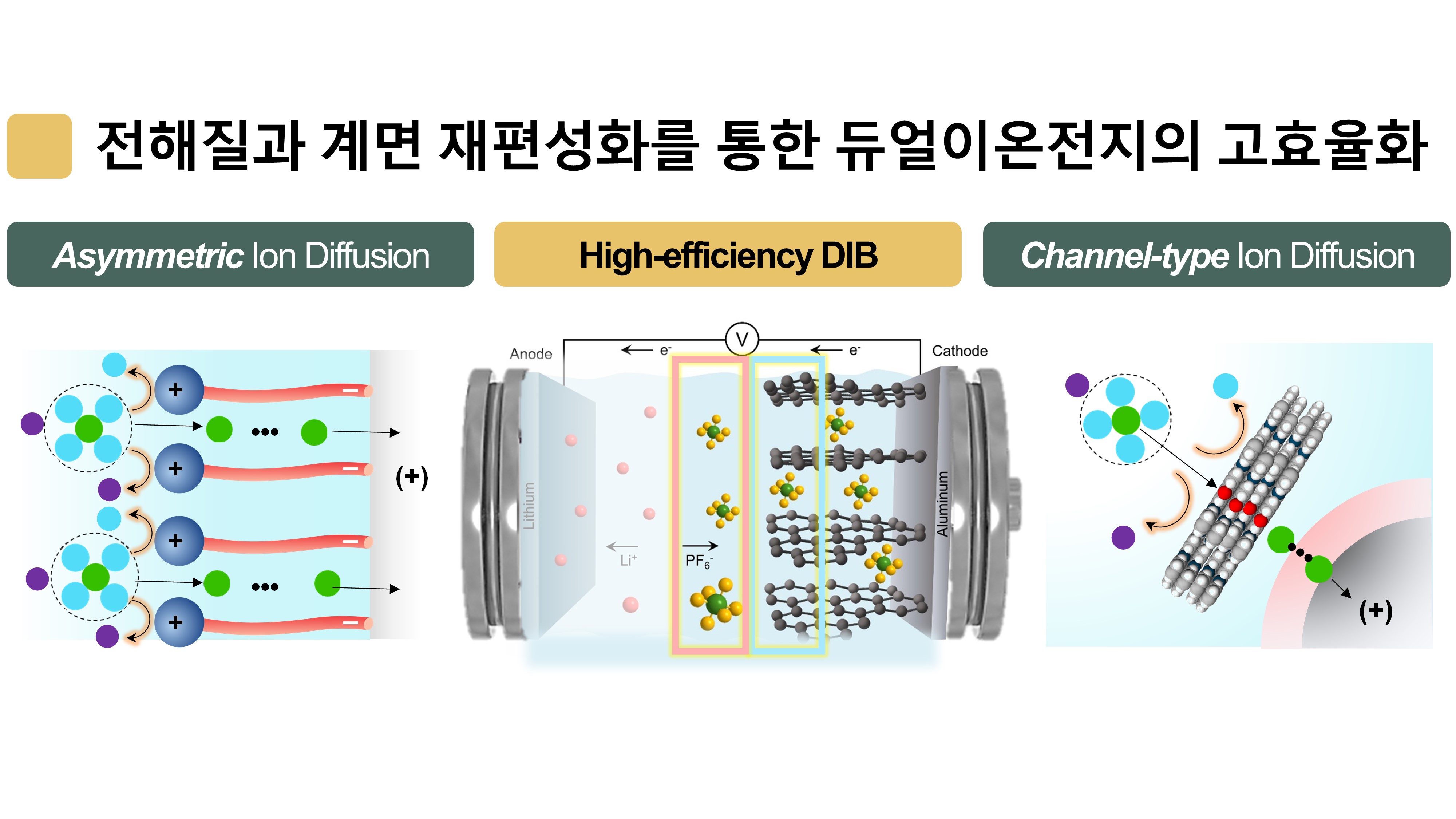
The global demand for dual-ion batteries, which could serve as power sources for next-generation electric vehicles, continues to rise steadily; however, there is a lack of related research in South Korea. Therefore, this study aims to develop a high-efficiency, stable dual-ion battery by reorganizing the electrode-electrolyte interface to enable fast and selective ion diffusion.
We plan to develop an electrolyte that allows for the asymmetric diffusion of lithium ions, solvent molecules, and anions by arranging an Electric-field Responsive Agent (ERA) at the interface. Further, we intend to implement electrode surface reorganization technology based on an organic framework structure by securing ion selectivity through a channel-type electrode surface protection layer.
Dual-ion batteries are an emerging field with the potential to serve as the foundational technology for new market creation and industrialization. Should this research be successfully realized, it could be applied to various devices that respond to internal electric fields and aqueous dual-ion batteries. It is also expected to contribute to acquiring high-capacity new material source technologies and hold significant industrial applicability.