Development of Ion Sponge-based CO₂ Conversion Electrocatalysts for C-N-S Ternary Bonding Chemicals Production

-
Affiliation
Korea University Department of Materials Science and Engineering
-
E-Mail
dnam@korea.ac.kr
- Homepage
Award-winning achievements
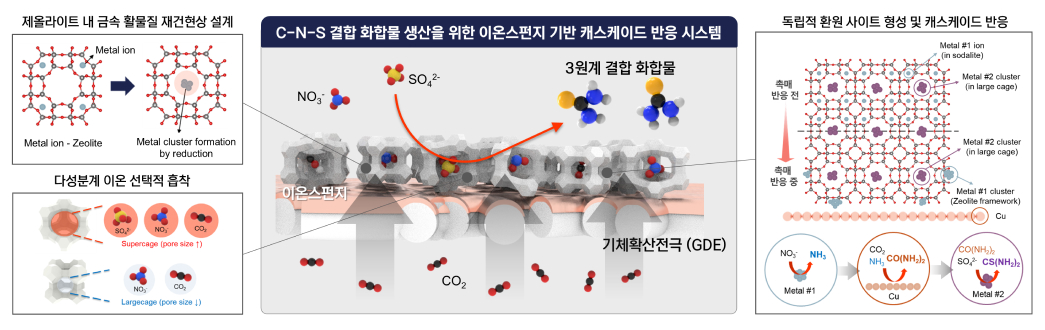
This project aims to design ion-sponge-based electrochemical catalysts for synthesis of multi-component compounds by induction of electrochemical reduction and bonding of ternary reactants through selective adsorption of multi-component reactants, provision of independent reduction sites, and local ion control on the catalyst surface.
To achieve this, systematic research will be conducted, including the design of thermodynamics-based zeolite reconstruction phenomena, the selective adsorption of multi-component ions through zeolites, and the creation of independent reduction sites through reconstruction phenomena and metal impregnation. The goal is to realize cascade C-N-S bonding reactions and open new horizons in CO₂ reduction by producing thiourea from CO₂.
The multi-component-reactant-based independent control technology secured through this research is expected to be applicable to the synthesis of various high-value-added compounds (C-N, C-N-S, C-N-Cl, and C-(N)-S-Cl, etc.) required by industry, specifically by directly utilizing nitrogen and sulfur pollutants in factory- or agricultural wastewater.